Why the strong Effect of Vitamin D on the Course of Infections has not yet been confirmed in Studies
Kiel, February 4th, 2024
“In our patients, when adjusted for age, gender, and comorbidities, Vitamin D deficiency was associated with a 6 fold higher hazard of severe course of disease and a about 15 fold higher risk of death.”
This is the most important sentence from the study by the University Hospital of Heidelberg, which monitored the course of infection in 185 #Covid 19 patients. “Vitamin D Deficiency and Outcome of Covid 19 Patients.”
There are about 30 observational studies with similar results, which are actually the best reflection of what happens in everyday life#.
The most important of these studies is one from Israel, which first looked for risk factors for a severe course of Covid 19 infection in the Israeli database, and then tested the factors found on the basis of the predicted and actual course of 253 Covid 19 patients.
It will surprise many that only 4 factors were found to predict the course of an infection with 82% accuracy. The two main factors were age and vitamin D levels (secondary factors were diabetes and COPD), and you can read here how the other risk factors mentioned, such as comorbidities (previous illnesses, parodontitis …), fit in.
Israeli study … main factors for progression … are vitamin D status and age (German Language).
The fact that this study used historical vitamin D levels (i. e. levels before the start of the infection) makes the Israeli study particularly valuable, because most other studies use vitamin D levels from the day of hospital admission, which is usually not the first day of infection.
This leads to criticism because it is not certain that the level recorded in the study is the pre infection level.
This criticism is justified because it has been observed that vitamin D levels drop drastically during an infection, as nutritionist Prof Martin Smollich (UKSH Schleswig Holstein) already stated in October 2020.
Covid 19 and low Vitamin D levels: consequence or cause? (Language German)
“In the context of the immunological acute phase reaction, the vitamin D level drops drastically in the short term, which is why a low vitamin D level is the consequence (and not the cause) of Covid 19 disease.”
The medical term for this is “negative acute phase reactant”. There is a publication on this in “The cleveland Clinic Journal” from February 2023.
The constellation of Vitamin D, the acute ?hase Response, and Inflammation
This is also mentioned in this very new study (31 January 2024)
Rickets Types and Treatment with Vitamin D and Analogues
Serum 25(OH)D is a negative acute phase reactant which has implications for acute and chronic inflammatory diseases; it is an unreliable biomarker of vitamin D status after an acute inflammatory insult. Hypovitaminosis D may be the consequence rather than the cause of chronic inflammatory diseases
In 2020, there were no concrete data on how quickly vitamin D levels fall during a Covid 19 infection, but this has changed since mid 2022.
Study from the University of Bratislava
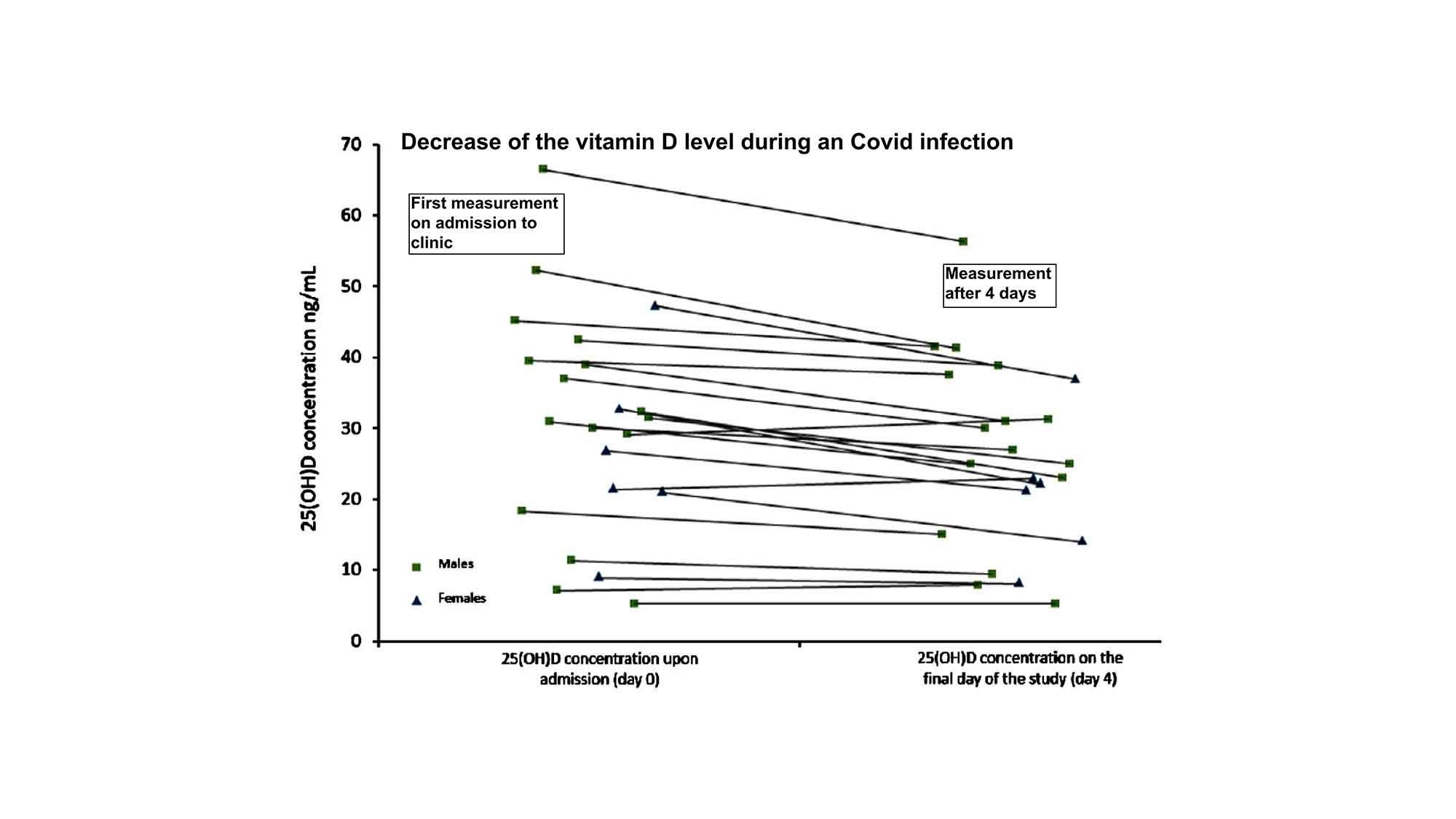
Serum 25 hydroxyvitamin D Concentration Significantly Decreases in Patients with Covid 19 Pneumonia during the First 48 Hours after Hospital Admission.
In Figure3 of the study, which is also used in the header of this publication, it can be seen that the 25(OH)D value (vitamin D in blood) can drop by up to 10 nanograms per millilitres in 4 days.
Here are a few key points that are important below
In 4 days, the 25(OH)D value dropped by 10 nanograms per millilitres, that is 2.5 nanograms per millilitres per day
With a 25(OH)D value of 22 nanograms per millilitres in winter (average population), the range of severe deficiency (less than 12 nanograms per millilitres) can be already reached on the 4th day of infection (22 4 by 2.5 equals 12), in summer on the 8th day.
To compensate for this loss, a person weighing 72 kg would need to take 25,000 I. U. of vitamin D a day. In general: 350 I. U. per kilograms of body weight.
As a severe vitamin D deficiency is closely associated with the occurrence of sepsis and the reactivation of the Epstein Barr virus (Long Covid, diabetes), this can easily explain the high Covid 19 mortality and the occurrence of Long Covid after an infection. Sepsis, Cytokine Storm.
Dr. med. Michael Nehls september 8th, 2021: Interview: Corona effective protection with vital substances? (Language German).
Reactivation of Epstein ##Barr virus: Treatment of Infectious…with High Dose Vitamin D3 …
Vitamin D can prevent EBV reactivation and Vitamin D is considered to have direct antiviral effects on envelop viruses [17]. With adequate vitamin D appropriate proteins like cathelicidins are encoded to rid the body of infection and prevent complications at the time of infection and in the future.
It would therefore be plausible to assume that the main reason for a severe course of infection and a long Covid is simply a vitamin D deficiency that occurs during an #infection.
Logically, the higher the vitamin D level prior to infection, the later this severe vitamin D deficiency occurs, which is why it has been observed that patients with higher vitamin D levels are less likely to become seriously ill.
This is an indirect effect of having a good level of vitamin D, because having a lot of vitamin D helps here mainly by delaying the onset of a deficiency, thus increasing the likelihood that an infection will be over before a deficiency occurs.
However, many medical professionals may not be aware of this connection and may only observe that higher doses of vitamin D appear to be beneficial. Therefore, they attempt to demonstrate through traditional intervention studies that vitamin D supplementation can improve survival rates for Covid 19 infections.
So one group gets something (vitamin D group) and the other group (placebo) does not, but because vitamin D measurement is relatively expensive, regular measurement of 25(OH)D is not done, so it is not recorded how this changes in the two groups.
It is usually found that vitamin D supplementation is helpful, but there is not a huge difference between the groups.
The exceptions are studies that use high doses of calcidiol (quickly usable storage form of vitamin D) or calcitriol (active Form of Vitamin D). These studies usually find an effect similar to that seen in observational studies, demonstrating that vitamin D supplementation may also be causally effective.
3 Studies on this
Spain: Effect of calcifediol treatment. Of the patients treated with calcifediol, none died, and all were discharged, without complications. The 13 patients not treated with calcifediol, who were not admitted to the ICU, were discharged. Of the 13 patients admitted to the ICU, two died and the remaining 11 were discharged.
USA: A randomized pilot study using calcitriol in hospitalized Covid 19 patients. There were 3 deaths and 4 readmissions in the control group and 0 deaths and 2 readmissions in the calcitriol group.
Japan: The effect of 1 hydroxy vitamin D treatment in hospitalized.
In the majority of intervention studies, only vitamin D in the form D3 (Cholecalciferol) is administered, which is normally available over the counter.
Because only a small effect of supplementation has been observed, there is currently no general recommendation for vitamin D supplementation.
But there are some reasons why only a small effect was found. The most important is the time factor because of the rapid drop in vitamin D levels.
Before Covid 19 infected patients are hospitalized and included in an intervention study, they have usually already had a few days of infection. As hospitalization usually only occurs when the course of an infection worsens, severe damage from sepsis may already be present at this point, which is no longer reversible.
As a result, it is not possible to detect as large a difference in intervention studies as in observational studies.
If sufficient vitamin D supplementation was started immediately after the onset of infection, sepsis would not occur in the vitamin D group and mortality in this group would be much lower than in the comparison group.
The time factor also plays a major role when vitamin D is administered in the common form D3 (Cholecalciferol). This form must first be converted into the quickly usable storage form of vitamin D, calcidiol (25(OH)D), before it can be converted into the active form calcitriol.
This takes time, so that in spite of supplementation there may be an interim deficiency in the vitamin D group, which triggers sepsis. However, as it is not usual to measure vitamin D levels repeatedly, the deficiency is not noticed.
This may occur even more frequently than expected because only about 14,000 IU can be converted per day, but about 25,000 IU are absorbed daily. The 14,000 IU are taken from a Study that observed how long it takes for 100,000 IU of vitamin D3 to be converted to the fast acting storage form, calcidiol.
That was 7 days, so it can be concluded that only about 100,000 divided by 7 equals 14,000 I. U. can be converted per day. Magnesium could also play a role here, as it is needed for the conversion and the conversion rate could be higher at higher magnesium levels.
It could therefore be that the occurrence of a deficiency cannot be safely prevented even with a high vitamin D3 supplement, or can only be prevented if cofactors such as magnesium are available in sufficient quantities.
Finally, there are studies in which vitamin D supplementation did not work because the vitamin D group received significantly less than the daily consumption of 25,000 I.U., so that the time until a deficiency occurred was only slightly extended.
Because of the decreasing vitamin D levels, it is therefore crucial that supplementation is effective quickly in order to detect a significant difference between the two groups.
Therefore, studies in which the slow acting form of vitamin D3 is supplemented during an infection cannot be used to replicate the results of observational studies.
In order to demonstrate the high efficacy of vitamin D supplementation, intervention studies must administer sufficient amounts of vitamin D in the fast acting forms calcidiol or calcitriol as soon as possible after the onset of infection to reliably prevent the development of sepsis. This is why the 3 trials using calcidiol or calcitrol showed such a good effect.
Thus, the evidence that vitamin D supplementation can largely prevent a severe course has already been established, and it is not justified to doubt these studies because of the poorer results of studies with the slow acting form of D3.
It is therefore time for a recommendation of vitamin D supplementation for the entire population, which can largely prevent a deficiency that occurs during an infection.
It could be recommended to supplement 350 I. U. per kilogram body weight (e. g. 72 kilograms 25,000 I. U.) if there are signs of an infection. But as long as it is not clear that a deficiency can be safely prevented, increasing the vitamin D level to 50 nanograms per millilitres is the better option.
A 25(OH)D value can be calculated based on daily use during an infection. Assuming that the acute phase of an infection lasts a maximum of 15 days, a 25(OH)D value can be calculated from which a severe deficiency does not occur. 12 nanograms per millilitres plus 15 by 2.5 nanograms per millilitres equals approximately 50 nanograms per millilitre.
This fits with the result of this Study from Germany with the headline “Covid 19 Mortality Risk Correlates Inversely with Vitamin D3 Status, and a Mortality Rate Close to Zero Could Theoretically Be Achieved at 50 nanograms per millilitres 25(OH)D3: Results of a Systematic Review and Meta Analysis”.
And also to the experiences of Indian doctors who have published many studies on the effects of vitamin D supplementation (typically 60,000 I. U. per day) during the pandemic.
The Hindu: High Vitamin D levels reduce Covid infection: NIMS study. Dr. Maheshwar also observed that less than 5% of people contracted the Covid 19 if the Vitamin D level was more than 55 nanograms per millilitres in them. The mortality of Covid patients is almost zero if Vitamin D level was 60 nanograms per millilitres and it is very high if the levels are less than 30 nanograms per millilitre.
As a severe deficiency is also associated with the development of autoimmune diseases, an effective recommendation for vitamin D supplementation would drastically reduce the incidence of autoimmune diseases caused by infections.
The cause of many autoimmune diseases is a reactivation of the Epstein Barr virus, which can easily be prevented by avoiding a severe vitamin D deficiency.
Treatment of Infectious Mononucleosis with High Dose Vitamin D3 …
Vitamin D can prevent EBV reactivation and Vitamin D is considered to have direct antiviral effects on envelop viruses.
The sad part of the whole story is that a doctor from Bamberg (Germany) published a guide in 2020 recommending both a preventive increase in vitamin D levels and a greatly increased supplementation (80,000 I.U. per day) during an infection. Dr. Kersten Bamberg: Covid 19 This is what you can do! (German Language).
Unfortunately, neither the mainstream press has reported on this guidance, nor have officials used this guidance as a template for creating an effective recommendation for vitamin supplementation, which would have resulted in far fewer deaths and autoimmune disease.
Furthermore, the hundred year history of vitamin D stands in the way of progress in research, because many people cannot imagine that the importance of vitamin D for infections was not recognized much earlier.
The reason for the occurrence of a severe deficiency can be easily explained by the viral load, which is often higher with a Covid 19 infection than with known infections. The more viruses, the more T cells have to be activated and the more vitamin D is being used. Accordingly, a severe deficiency occurs more often.
The effect that leads to increased vitamin D use during an infection is also known in detail.
Some cells constantly extract vitamin D from the blood via a vitamin D receptor (VDR), but T cells (T lymphocytes) only release a vitamin D receptor once they have been activated to fight viruses.
Anti Inflammatory Effects of 1,25(OH)2D/Calcitriol in T Cell Immunity
Of note, resting monocytes and dendritic cells express an intracellular VDR whereas resting T and B lymphocytes express little to no VDRs. Accordingly, in our experiments we observed no or a low expression of the VDR in the resting T cells, as determined by a Western blot analysis. After T lymphocyte activation with anti CD3 mAb, we observed a significant increase in the VDR expression level induced by a treatment with calcitriol.
Since a T cell can only fight a limited number of viruses, the greater the viral load to be fought, the more T cells have to be activated, which leads to a corresponding increase in vitamin D use.
However, it has been commonly believed that vitamin D levels change slowly. Therefore, even doctors conducting studies do not check to see if vitamin D levels change rapidly during an infection. This creates a vicious circle, as the missing measurement makes it impossible to realize that there are still gaps in the knowledge that has been taught.
Many of the correlations mentioned here were already known before the start of the pandemic, and by May 2020 at the latest, when it became known that a severe course of a Covid 19 infection does not develop linearly, and that there is a day on which the course suddenly worsens, one could have come up with the idea that something that is urgently needed by the immune system comes to an end on that day.
Even then it was obvious that this could be vitamin D, but when it is only about food supplements, with which there is not much money to be made, many brains remain switched off. So more than 2 years have passed since then, without the easily recognizable mechanism of vitamin D consumption being considered in studies.
Until then, everyone will continue to be surprised that all possible consequences of a vitamin D deficiency such as sepsis, autoimmune diseases, diabetes, hair loss, muscle pain, high blood pressure etc. are observed after infections, and that in the first six months after an infection the risk of getting another infection is higher, which is then typically more severe (due to lower vitamin D levels after infection).
My hope is that in the future more doctors will come up with the idea of measuring the vitamin D level of Covid 19 patients several times during an infection because they have heard that vitamin D is a “negative acute phase reactant” and would like to check this for themselves.
What comes out can be read in the commentary by Klaus Schneider on the publication behind the following link, who supplemented an estimated 18,000 I. U. daily during his Covid 19 infection to increase his vitamin D level.
Vitamin D Pillen – Segen oder Abzocke? (German Language).
“Before my corona infection, I had a vitamin D level of 65 nanograms per millilitres. When my test came back positive, I immediately increased my daily dosage threefold to reach a level of 90 nanograms per millilitres. I wanted to support the immune system in its defense against viruses. After my corona infection, I had my vitamin D blood levels checked again at my own expense and my level was not 90 nanograms per millilitres, as it should have been, but still at 62.3 nanograms per millilitres. For me, this was a clear sign that the body needs significantly more vitamin D during an infection to defend itself against viruses. I had a harmless course. I would therefore like to thank you, Mr. Wiechering, for your detailed explanations, which confirm my personal experiences during the virus infection. Yours sincerely
Klaus Schneider”.
If anyone has had similar experiences, I would be pleased to receive an e mail or a comment under this publication.
Further information on Covid 19 and Long Covid can be found at www.kiwiw.de …
Christian Wiechering, Kiel (Germany)



































 Gütsel RSS Feed
Gütsel RSS Feed